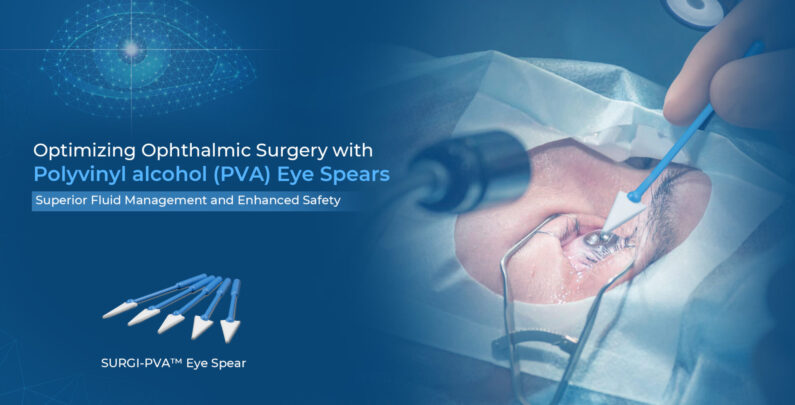
Optimizing Ophthalmic Surgery with PVA Eye Spears: Superior Fluid Management and Enhanced Safety

In ophthalmic surgery, maintaining a clear surgical field is paramount. Whether performing cataract extraction, LASIK, trabeculectomy, or vitreoretinal procedures, even small amounts of fluid can obscure the surgeon’s view, compromise precision, and risk damage to delicate eye tissues. Traditional tools such as suction devices and ophthalmic viscosurgical devices (OVDs) often face challenges like pressure fluctuations, suction loss, or microtrauma.1-3
This is where Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Eye Spears, particularly SURGI-PVA™ Eye Spears, are designed to enhance fluid management and surgical safety, offering superior absorption and ensure surgical safety.4
Why PVA Eye Spears Outperform Cellulose Alternatives
Cellulose-based spears can absorb fluids effectively, but their major drawback lies in microscopic fragmentation. These tiny residues may trigger postoperative inflammation, foreign body reactions, or microbial contamination ultimately delaying recovery.
In contrast, PVA spears are ultra-clean, residue-free, and tissue-friendly, offering significant clinical advantages4,5:
| Feature | PVA Spears (SURGI-PVA™) | Cellulose Spears |
| Absorption efficiency | High absorption with well retain fluid | Good absorption with Less fluid retention |
| Risk of fragmentation | None (no shedding) | Fiber shedding risk |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, non-irritant | Generally biocompatible but may causing tissue irritation |
| Tissue safety | Gentle on ocular tissues | Risk of inflammation, scarring or blebitis |
| Flexibility | Exhibits excellent flexibility and tensile strength, making it suitable for delicate procedures | Generally, less flexible; maintains rigidity during use |
Understanding SURGI-PVA™ Eye Spears
SURGI-PVA™ Eye Spears are ultra-clean, highly porous sponges with better liquid retention, strong chemical resistance, and efficient wicking, made using advanced Air Foam Technology.
 Fig 1: SURGI-PVA™ Eye Spear
Fig 1: SURGI-PVA™ Eye Spear
Characteristics of SURGI-PVA™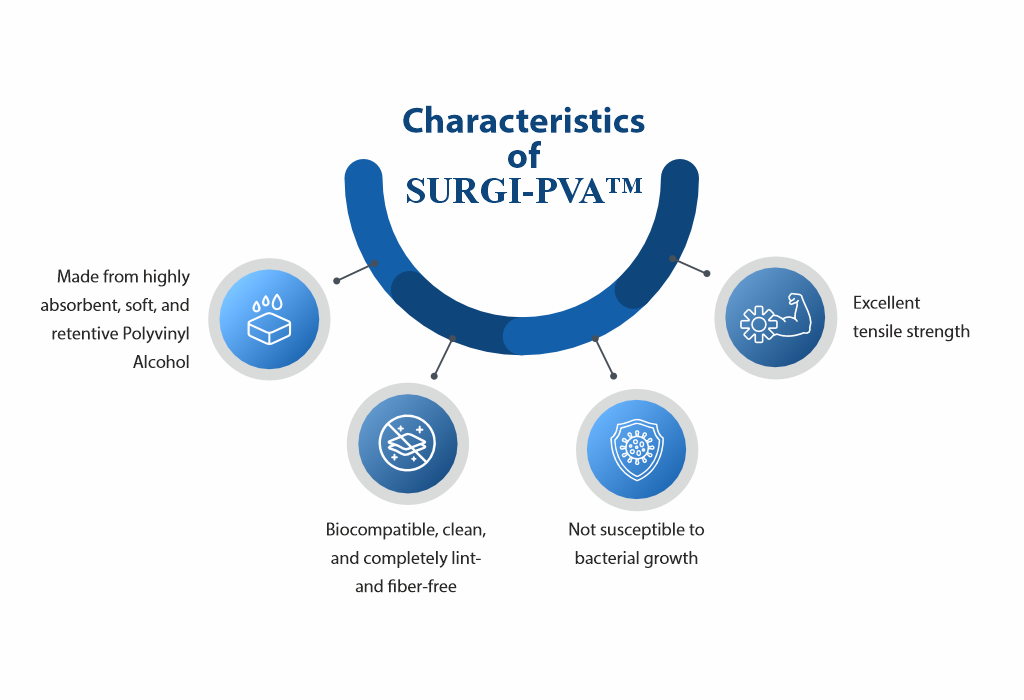 Key Features & Benefits
Key Features & Benefits
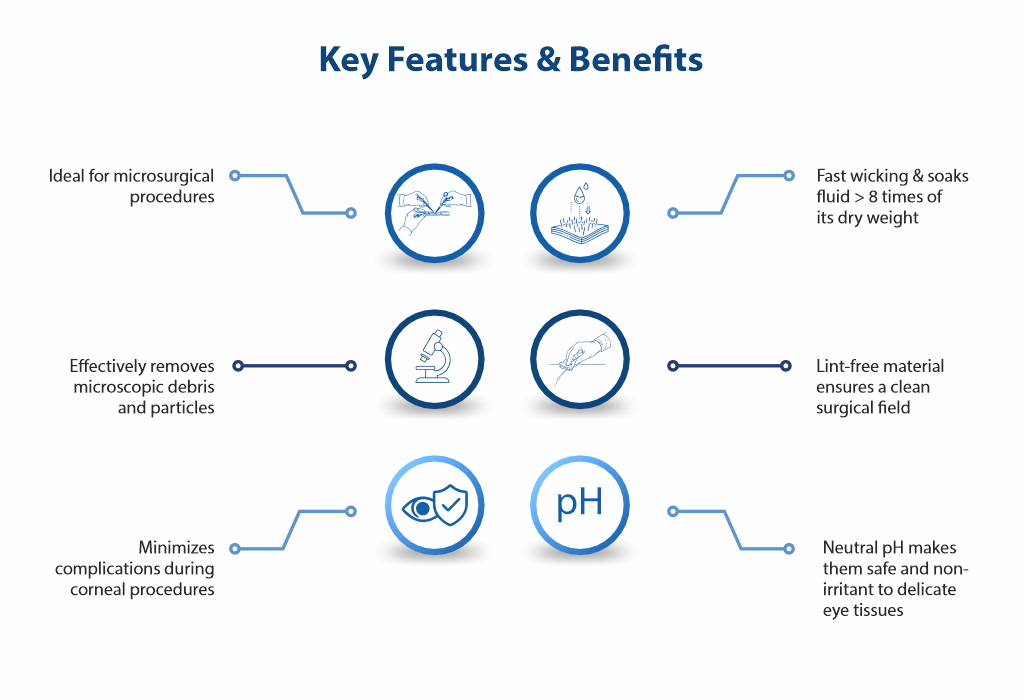 PVA Sponge Applications in Ophthalmic Surgery4-5
PVA Sponge Applications in Ophthalmic Surgery4-5
Beyond fluid management, PVA sponges have expanded clinical utility:
- Flap adherence in LASIK – ensures corneal flap stability
- Wound healing support – scaffold for ocular tissue repair
- Drug delivery – provides sustained, localized delivery of therapeutic agents.
- Biopsy & research – reduces contamination, aids cellular analysis
- Alternative biomaterial – useful in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering
Conclusion
In ophthalmic surgery, the choice of tools directly impacts precision and patient outcomes. SURGI-PVA™ Eye Spears offer superior fluid management, safeguard delicate ocular tissues, and reduce surgical complications. Incorporating SURGI-PVA™ into practice enhances surgical efficiency, accuracy and overall quality of care, supporting better outcomes for both surgeons and patients.
References:
- Shafeena P, Venkataramanan P, Murugesan S, Gosalia H, Chandrakanth P, Venkatapathy N. EYESPIRATOR-A novel do-it-yourself suction device. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2023 Dec 1;71(12):3715-7.
- Hejsek L, Kadlecova J, Sin M, Velika V, Jiraskova N. Intraoperative intraocular pressure fluctuation during standard phacoemulsification in real human patients. Biomedical Papers. 2019 Feb 18;163(1):75-9.
- Malvankar-Mehta MS, Fu A, Subramanian Y, Hutnik C. Impact of ophthalmic viscosurgical devices in cataract surgery. Journal of ophthalmology. 2020;2020(1):7801093.
- Poole TR, Gillespie IH, Knee G, Whitworth J. Microscopic fragmentation of ophthalmic surgical sponge spears used for delivery of antiproliferative agents in glaucoma filtering surgery. British journal of ophthalmology. 2002 Dec 1;86(12):1448-9.
- Sachdev GS, Ramamurthy S. Small incision lenticule extraction–Current perspective. Kerala Journal of Ophthalmology. 2019 Sep 1;31(3):176-81.
- Karimi A, Navidbakhsh M, Faghihi S. RETRACTED: Fabrication and mechanical characterization of a polyvinyl alcohol sponge for tissue engineering applications. Perfusion. 2013;29(3):231-237. doi:1177/0267659113513823